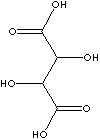
|
Tartaric Acid, also called dihydroxysuccinic acid [HOOC(CHOH)2COOH]), is a white
crystalline naturally occurring carboxylic acid; melting at 171 C, soluble in
water and alcohols. It is obtained natually as a by-products of wine
fermentation along with its salts. This natural acid is used as an antioxidant
in food. Tartaric acid has two asymmetrical carbon atoms and three chiral
isomers; the dextro-, levo-, (optically active) and meso- forms (optically
inactive). The d- and l-tartaric acids are said to be enantiomorphs (each
molecule is asymmetrical and has the mirror image of the other). There are two
asymmetrical carbon atoms in meso-tartaric acid, but the molecule is symmetrical
and does not exhibit optical activity; the optical activity is internally
compensated, the effect of one asymmetrical carbon atom balancing the effect of
the other. A pair of optical isomers such as d-tartaric acid and meso-tartaric
acid, which are not enantiomorphs, are called diastereoisomers. Tartaric Acid is
a useful raw material for the synthesis of other chiral compounds. L-tartaric
acid (called also d-2,3-dihydroxysuccinic acid or l-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic
acid) is chiefly found in many plant especially grape. This form can be
partially converted to the others by heating it with an aqueous alkali
(potassium hydroxide) as the isomeric forms differ from each other in boiling
points. It can be synthesized by the reaction of maleic acids or fumaric acids
with aqueous potassium permanganate. Tartaric acid is biodegradable and no
pollution problems are known. Tartaric acid is used chiefly in the form of its
salts, e.g., cream of tartar (potassium hydrogen tartrate), Rochelle salt
(potassium sodium tartrate) and Tartar Emetic (antimony potassium tartrate). It
is used to enhance flavours in foods, confectionery and beverages. It is used as
a chemical intermediate and a sequestrant and in tanning, ceramics, photography,
textile processing, mirror silvering, and metal coloring. |